sift
A tool to model and analyze the design of systems from java class files.
Spring-Boot with Axon Framework instrumenter in action.
Entity and Entity Type
The system model is described by its constituent entities and their relationships. Each entity is uniquely identified by either a class, method, field or parameter element; an element can not be associated with more than one entity.
All entities are mapped to a type. A type represents any notable part of the system, e.g. REST controllers, HTTP endpoints, inbound/outbound messages, RDS etc.
$ sift --instrumenter spring-axon --list-entity-types target/classes
entity types of spring-axon
1 aggregate
2 aggregate-ctor
1 aggregate-member
6 command
6 command-handler
1 controller
13 endpoint
7 event
7 event-handler
7 event-sourcing-handler
1 projection
3 query
4 query-handler
Instrumenter pipelines
Instrumenter Pipelines are responsible for producing the system model from input classes. Pipelines are written in a declarative DSL, which provides high-level abstractions for identifying and interrelating entities from class structure or usage.
val controller = Entity.Type("controller")
val endpoint = Entity.Type("endpoint")
instrumenter {
// iterate over all input classes
classes {
annotatedBy<RestController>() // filter classes
entity(controller) // mark remaining as 'controller'
methods { // iterate all controller methods
annotatedBy<Endpoint>() // filter @Endpoint methods
entity(endpoint)
// associate controllers with their endpoints
controller["endpoints"] = endpoint
}
}
}
Input elements – classes, methods, parameters and fields – are processed in batch, line-by-line.
A Instrumenter Pipeline can be expressed in about 100LOC. Some are notably shorter, e.g. jpa
and jdbi. Any pipeline can be included by user-defined pipelines using include(pipeline).
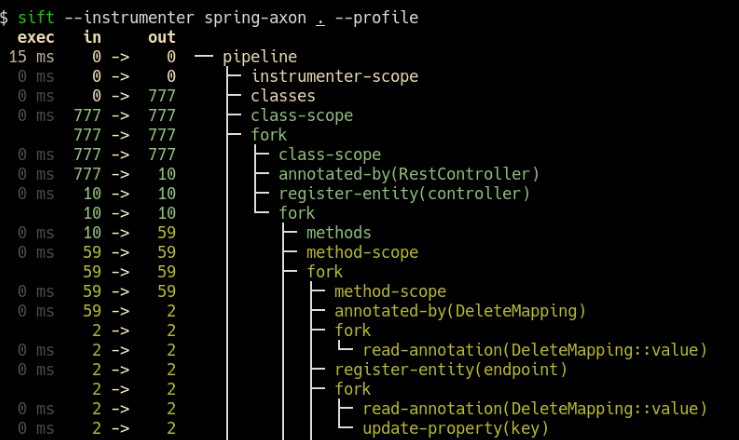
The execution of an Instrumenter Pipeline can be visualized with --profile:
Features
Caveats and limitations
- no flow control