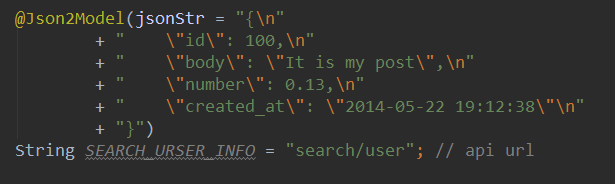
Moshi
Moshi is a modern JSON library for Android and Java. It makes it easy to parse JSON into Java
objects:
And it can just as easily serialize Java objects as JSON:
Built-in Type Adapters
Moshi has built-in support for reading and writing Java’s core data types:
- Primitives (int, float, char...) and their boxed counterparts (Integer, Float, Character...).
- Arrays, Collections, Lists, Sets, and Maps
- Strings
- Enums
It supports your model classes by writing them out field-by-field. In the example above Moshi uses
these classes:
to read and write this JSON:
The [Javadoc][javadoc] catalogs the complete Moshi API, which we explore below.
Custom Type Adapters
With Moshi, it’s particularly easy to customize how values are converted to and from JSON. A type
adapter is any class that has methods annotated @ToJson and @FromJson.
For example, Moshi’s default encoding of a playing card is verbose: the JSON defines the rank and
suit in separate fields: {"rank":"A","suit":"HEARTS"}. With a type adapter, we can change the
encoding to something more compact: "4H" for the four of hearts or "JD" for the jack of
diamonds:
Register the type adapter with the Moshi.Builder and we’re good to go.
Voilà:
Another example
Note that the method annotated with @FromJson does not need to take a String as an argument.
Rather it can take input of any type and Moshi will first parse the JSON to an object of that type
and then use the @FromJson method to produce the desired final value. Conversely, the method
annotated with @ToJson does not have to produce a String.
Assume, for example, that we have to parse a JSON in which the date and time of an event are
represented as two separate strings.
We would like to combine these two fields into one string to facilitate the date parsing at a
later point. Also, we would like to have all variable names in CamelCase. Therefore, the Event
class we want Moshi to produce like this:
Instead of manually parsing the JSON line per line (which we could also do) we can have Moshi do the
transformation automatically. We simply define another class EventJson that directly corresponds
to the JSON structure:
And another class with the appropriate @FromJson and @ToJson methods that are telling Moshi how
to convert an EventJson to an Event and back. Now, whenever we are asking Moshi to parse a JSON
to an Event it will first parse it to an EventJson as an intermediate step. Conversely, to
serialize an Event Moshi will first create an EventJson object and then serialize that object as
usual.
Again we register the adapter with Moshi.
We can now use Moshi to parse the JSON directly to an Event.
Parse JSON Arrays
Say we have a JSON string of this structure:
We can now use Moshi to parse the JSON string into a List<Card>.
Fails Gracefully
Automatic databinding almost feels like magic. But unlike the black magic that typically accompanies
reflection, Moshi is designed to help you out when things go wrong.
JsonDataException: Expected one of [CLUBS, DIAMONDS, HEARTS, SPADES] but was ANCHOR at path $.visible_cards[2].suit
at com.squareup.moshi.JsonAdapters$11.fromJson(JsonAdapters.java:188)
at com.squareup.moshi.JsonAdapters$11.fromJson(JsonAdapters.java:180)
...
Moshi always throws a standard java.io.IOException if there is an error reading the JSON document,
or if it is malformed. It throws a JsonDataException if the JSON document is well-formed, but
doesn’t match the expected format.
Built on Okio
Moshi uses [Okio][okio] for simple and powerful I/O. It’s a fine complement to [OkHttp][okhttp],
which can share buffer segments for maximum efficiency.
Borrows from Gson
Moshi uses the same streaming and binding mechanisms as [Gson][gson]. If you’re a Gson user you’ll
find Moshi works similarly. If you try Moshi and don’t love it, you can even migrate to Gson without
much violence!
But the two libraries have a few important differences:
- Moshi has fewer built-in type adapters. For example, you need to configure your own date
adapter. Most binding libraries will encode whatever you throw at them. Moshi refuses to
serialize platform types (java.*,javax.*, andandroid.*) without a user-provided type
adapter. This is intended to prevent you from accidentally locking yourself to a specific JDK or
Android release. - Moshi is less configurable. There’s no field naming strategy, versioning, instance creators,
or long serialization policy. Instead of naming a fieldvisibleCardsand using a policy class
to convert that tovisible_cards, Moshi wants you to just name the fieldvisible_cardsas it
appears in the JSON. - Moshi doesn’t have a
JsonElementmodel. Instead it just uses built-in types likeListand
Map. - No HTML-safe escaping. Gson encodes
=as\u003dby default so that it can be safely
encoded in HTML without additional escaping. Moshi encodes it naturally (as=) and assumes that
the HTML encoder – if there is one – will do its job.
Custom field names with @Json
Moshi works best when your JSON objects and Java objects have the same structure. But when they
don't, Moshi has annotations to customize data binding.
Use @Json to specify how Java fields map to JSON names. This is necessary when the JSON name
contains spaces or other characters that aren’t permitted in Java field names. For example, this
JSON has a field name containing a space:
With @Json its corresponding Java class is easy:
Because JSON field names are always defined with their Java fields, Moshi makes it easy to find
fields when navigating between Java and JSON.
Alternate type adapters with @JsonQualifier
Use @JsonQualifier to customize how a type is encoded for some fields without changing its
encoding everywhere. This works similarly to the qualifier annotations in dependency injection
tools like Dagger and Guice.
Here’s a JSON message with two integers and a color:
By convention, Android programs also use int for colors:
But if we encoded the above Java class as JSON, the color isn't encoded properly!
The fix is to define a qualifier annotation, itself annotated @JsonQualifier:
Next apply this @HexColor annotation to the appropriate field:
And finally define a type adapter to handle it:
Use @JsonQualifier when you need different JSON encodings for the same type. Most programs
shouldn’t need this @JsonQualifier, but it’s very handy for those that do.
Omit fields with transient
Some models declare fields that shouldn’t be included in JSON. For example, suppose our blackjack
hand has a total field with the sum of the cards:
By default, all fields are emitted when encoding JSON, and all fields are accepted when decoding
JSON. Prevent a field from being included by adding Java’s transient keyword:
Transient fields are omitted when writing JSON. When reading JSON, the field is skipped even if the
JSON contains a value for the field. Instead it will get a default value.
Default Values & Constructors
When reading JSON that is missing a field, Moshi relies on the the Java or Android runtime to assign
the field’s value. Which value it uses depends on whether the class has a no-arguments constructor.
If the class has a no-arguments constructor, Moshi will call that constructor and whatever value
it assigns will be used. For example, because this class has a no-arguments constructor the total
field is initialized to -1.
If the class doesn’t have a no-arguments constructor, Moshi can’t assign the field’s default value,
even if it’s specified in the field declaration. Instead, the field’s default is always 0 for
numbers, false for booleans, and null for references. In this example, the default value of
total is 0!
This is surprising and is a potential source of bugs! For this reason consider defining a
no-arguments constructor in classes that you use with Moshi, using @SuppressWarnings("unused") to
prevent it from being inadvertently deleted later:
Kotlin
Moshi is a great JSON library for Kotlin. It understands Kotlin’s non-nullable types and default
parameter values. When you use Kotlin with Moshi you may use reflection, codegen, or both.
Reflection
The reflection adapter uses Kotlin’s reflection library to convert your Kotlin classes to and from
JSON. Enable it by adding the KotlinJsonAdapterFactory to your Moshi.Builder:
Moshi’s adapters are ordered by precedence, so you always want to add the Kotlin adapter after your
own custom adapters. Otherwise the KotlinJsonAdapterFactory will take precedence and your custom
adapters will not be called.
The reflection adapter requires the following additional dependency:
Note that the reflection adapter transitively depends on the kotlin-reflect library which is a
2.5 MiB .jar file.
Codegen
Moshi’s Kotlin codegen support is an annotation processor. It generates a small and fast adapter for
each of your Kotlin classes at compile time. Enable it by annotating each class that you want to
encode as JSON:
The codegen adapter requires that your Kotlin types and their properties be either internal or
public (this is Kotlin’s default visibility).
Kotlin codegen has no additional runtime dependency. You’ll need to [enable kapt][kapt] and then
add the following to your build to enable the annotation processor:
You must also have the kotlin-stdlib dependency on the classpath during compilation in order for
the compiled code to have the required metadata annotations that Moshi's processor looks for.
Limitations
If your Kotlin class has a superclass, it must also be a Kotlin class. Neither reflection or codegen
support Kotlin types with Java supertypes or Java types with Kotlin supertypes. If you need to
convert such classes to JSON you must create a custom type adapter.
The JSON encoding of Kotlin types is the same whether using reflection or codegen. Prefer codegen
for better performance and to avoid the kotlin-reflect dependency; prefer reflection to convert
both private and protected properties. If you have configured both, generated adapters will be used
on types that are annotated @JsonClass(generateAdapter = true).
Download
Download [the latest JAR][dl] or depend via Maven:
or Gradle:
Snapshots of the development version are available in [Sonatype's snapshots repository][snap].
ProGuard
If you are using ProGuard you might need to add the following options:
-dontwarn okio.**
-dontwarn javax.annotation.**
-keepclasseswithmembers class * {
@com.squareup.moshi.* <methods>;
}
-keep @com.squareup.moshi.JsonQualifier interface *
Additional rules are needed if you are using Kotlin:
...If you are using the reflect API (i.e. KotlinJsonAdapterFactory):
-keepclassmembers class kotlin.Metadata {
public <methods>;
}
...If you are using the codegen API (i.e. JsonClass(generateAdapter = true)):
-keep class **JsonAdapter {
<init>(...);
<fields>;
}
-keepnames @com.squareup.moshi.JsonClass class *