Composing clocks sample app
This is a sample app to show how to build an app that follows the practices described in the series of articles Compose (UI) beyond the UI.
These practices, in short, propose manually handling configuration changes and avoiding AAC ViewModels in apps that are fully in compose. To understand why, please read the articles (Part I, Part II, Part III).
This app uses mock data to save time on API requests, and to avoid needing credentials.
Project characteristics
- Compose UI for everything (beta01)
- MVVM architecture
- No usage of AppCompatActivity, Fragment or AAC ViewModel
- Config changes are manually handled: language or orientation changes do not recreate the activity
- Koin for DI and scoping screens and nav-graphs
- Coroutines and flow
- App state is saved, with utils that simplify usage with flow
- ViewModels that are scoped to screens, to screen-flows (nested graph) and to the whole app
- Navigation component (with helpers to manage koin scopes and route creation)
- Layout that adapts for landscape or multi-window (with a simple animation)
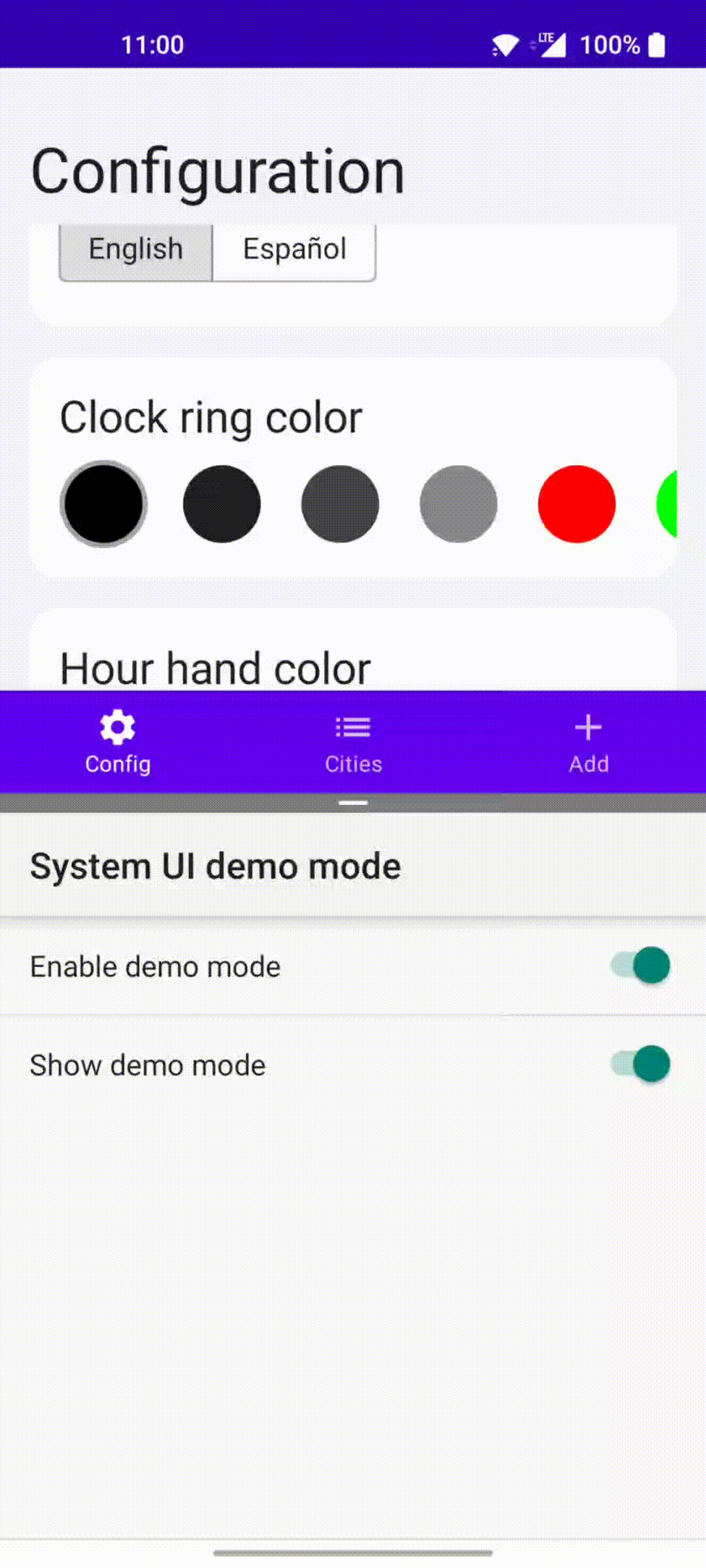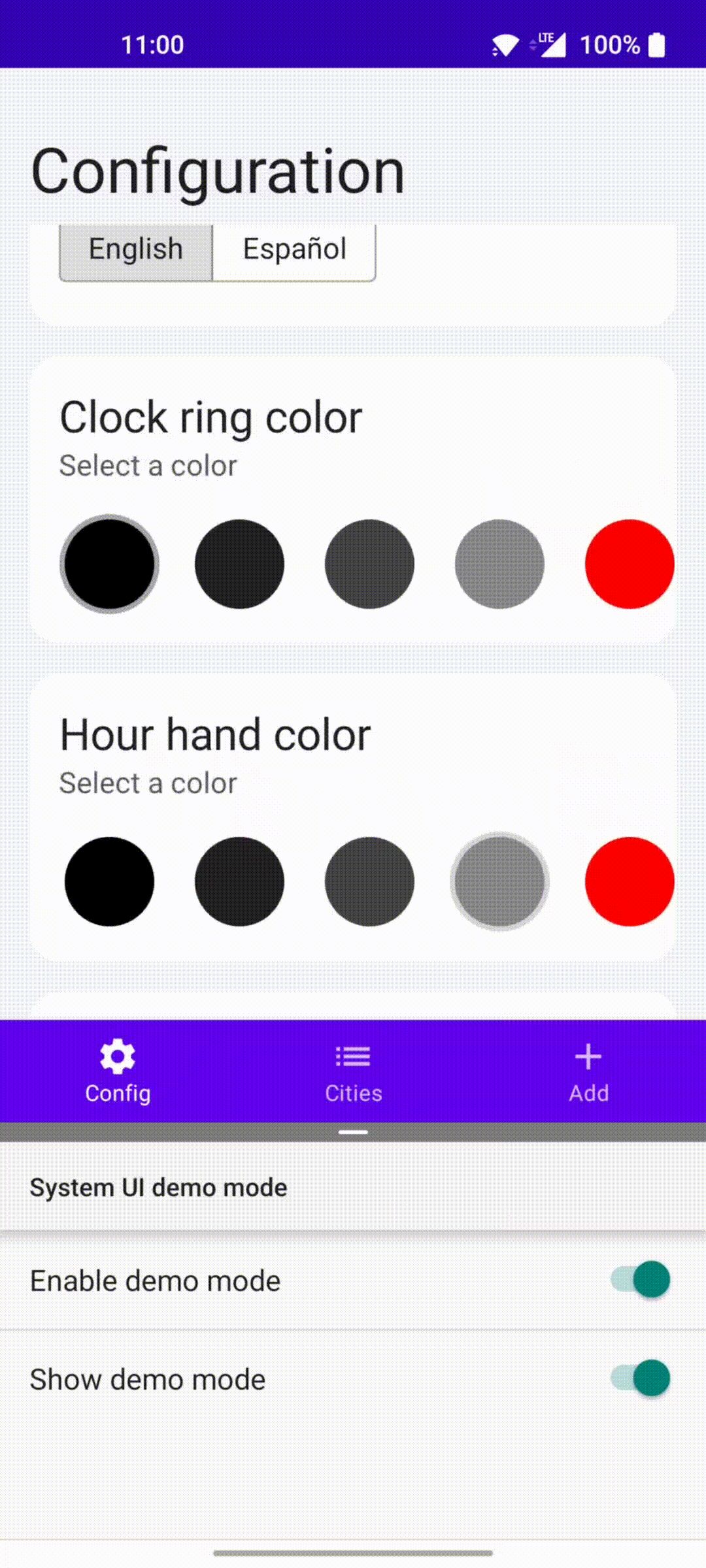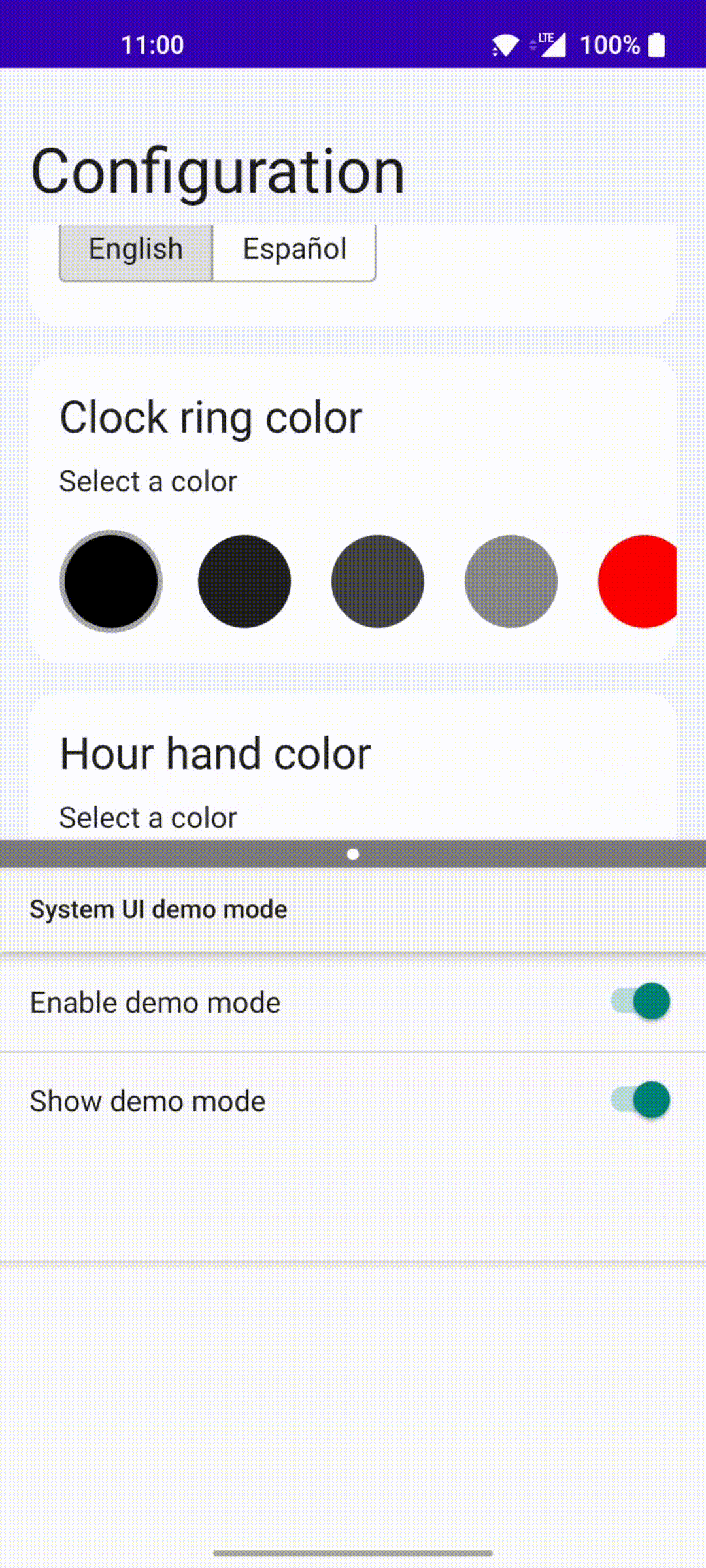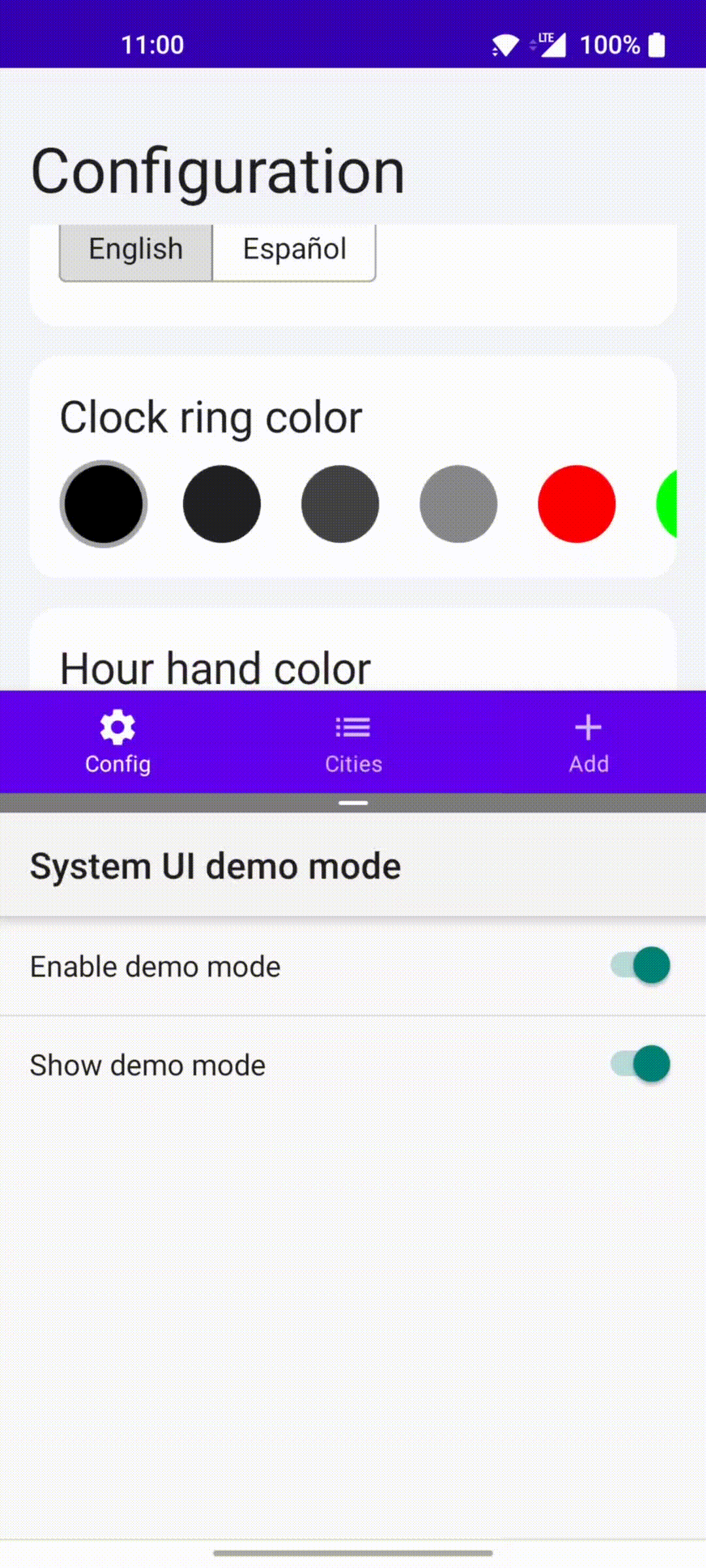
- Custom clock that can be themed
- Toggle to force a different locale without recreating the activity
- Bottom bar navigation that keeps correct selection on sub-screens
- Some simple animations (when resizing multiwindow in config screen, when time passes in clock, when choosing a clock type, or in picture previews)
- Coil with accompanist to display images
App description
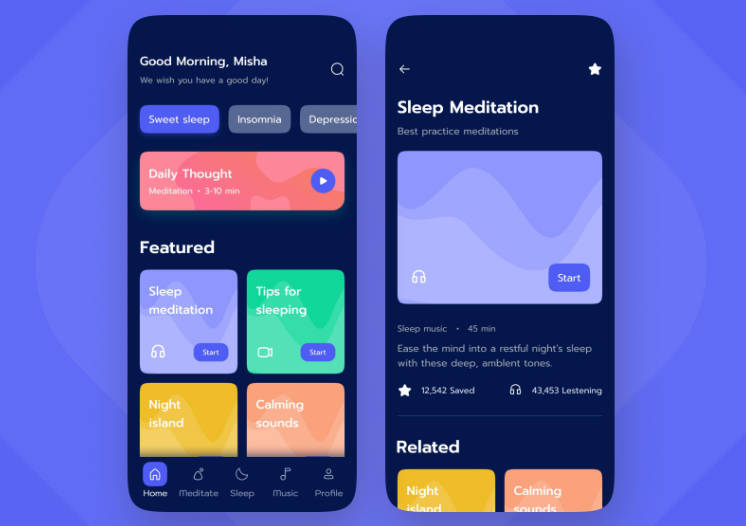
This app has a bottom navigation bar with three destinations. The first one is a configuration screen where you can change the language and theme the clock (change the color of some of its parts).
The second screen shows a list of cities with a picture and a clock that shows the local time. Clicking on a city takes the user to the screen detail where they can see the timezone and a description of the city.
Finally, the third bottom bar destination allows the user to add a city to the list. It consists of a flow of two screens, and it is possible to navigate back and forth without losing the data. In the first screen of this flow it is possible to write the city name, and select the timezone and clock style. Then, on the second screen the user can introduce a description and an URL for the picture, which can be previewed. Adding the city takes the user to the city list, with the new addition.
| Composing Clocks | Resizing |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Non-AAC ViewModels (or ViewControllers)
To build our own ViewModels we need the following:
- A way to retrieve the same instance while its lifecycle is alive, or in other words, while the user has not left the screen or view.
- A way to clear it when its lifecycle ends, to cancel ongoing tasks like coroutines.
- A way to save user state.
To obtain the same instance of the ViewController while its lifecycle is alive, in this sample Koin's scopes are used: getOrCreateScope. To know what instance to retrieve, the navigation path with the parameters filled is used as id.
To clear the ViewControllers and other scoped instances that require clearing, those instances implement the Clearable interface and are declared with bind Clearable::class in Koin.
To cancel the scope when the user exits a destination we have the utility RunOnce (which uses rememberSaveable) and then set a LifecycleEventObserver to the NavBackStackEntry of the destination.
To aid in this process there are some helpers that are further explained in navigation helpers.
Finally, to save state in ViewModels tied to a navigation destination we can retrieve a SavedStatHandle from the NavBackStackEntry. For other cases, compose provides rememberSaveable. To unify saving state this app has the interface StateSaver with two implementations, one for each case. This way the classes that need to save state do not have to worry about concrete implementations, and state saving is platform agnostic.
Forcing a locale
The app allows changing the language throuth a toggle (only Spanish and English). The language change is done without recreating the activity, which is faster and avoids flashing the screen.
In newer versions of Android, to force a change of locale you are supposed to use attachBaseContext, which relies on Activity recreation to work.
The alternative is to use resources.updateConfiguration, which is deprecated. This works without recreating the Activity, but it is deprecated due to problems encountered in WebView with night mode needing to change the resources configuration.
In compose there is a new way of changing the language, which is using CompositionLocalProvider and providing an updated context and layoutDirection. As of beta01, however, the bottom navigation bar in scaffold does not get updated when the locale is changed. It only gets updated when the screen orientation changes, for example.
I have opened this issue that you can star if it affects you, and currently I use the deprecated method. You can find an example with the deprecated approach in SetLanguage, and an example of the compose-like alternative -that does not work properly yet- in LanguageOverride.
Navigation helpers
This sample provides utilities to help handling scopes for screens and nested graphs in navigation. These helpers require using the provided models that help build navigation paths.
If you know how to navigate with Navigation component and how to use Koin scopes, the following sections describe the small changes you will need to apply, if you choose to use these helpers. Basically, you will need to use different functions to declare your destinations, declare classes to define each destination (that extend the proper parent), and declare Koin scopes in a specific manner. In exchange, you will get a scope that is automatically handled for your navigation destinations (screens and nested graphs); and an opinionated way of declaring destinations and arguments, that helps in building the paths.
Declaring a screen in a NavHost
It can be done with this syntax: scopedComposable(YourDestination) { navEntry, scope ->, where YourDestination is an instance of a class that extends NavDestination.
The scope parameter is a Koin scope that can be used to retrieve instances that are bound to the scope of the screen, like the ViewModel or other ViewController.
Declaring a nested graph in a NavHost
It can be done with this syntax: scopedNavigation(YourSubgraph) { nestedNavGraph ->, where YourSubgraph is an instance of a class that extends NestedNavGraph.
To declare destinations inside the nested graph you can use this:
Here YourDestination is also an instance of a class that extends NavDestination, and the nestedNavGraph is the parameter provided by scopedNavigation. You get two scopes, one for this screen and another for the nested graph. This way, if you need to scope a ViewController (or something else) to the whole screen flow it can be done with that scope.
Defining a screen destination
To declare a screen destination create an object that extends ScreenDestination or ScreenDestinationWithArgs, and specify the navigation route, the list of arguments (as NavArguments) and the params class.
The params class must extend NavParams and combine its parameters into a list in the same order as declared in the Destination arguments. If an argument is optional, to build the list use this: YourNavArgument.paramsAsRoute(paramVariable).
Defining a nested graph destination
To declare a nested graph destination create an object that extends SubgraphDestination or SubgraphDestinationWithArgs, and specify the navigation route, the list of arguments (as NavArguments), the start destination, and the params class for the subgraph and for the start destination.
Navigating to a destination with no parameters
You can use navController.navigate(YourDestination.buildRoute(NoParams)), or the less explicit YourDestination.declaredPath.
Navigating to a destination with parameters
You can pass YourDestination.buildRoute(DestinationNavParams(firstParam, secondParam)) to the navigate function.
Navigating to a destination with optional NavParams
If you have optional params you should declare them as OptionalParam in your NavParams. Then use OptionalParam.Provided(id) or OptionalParam.Default accordingly.
Declare a Koin scope for a screen
Pass the ScreenDestination as scope qualifier. Then in all your scoped instances that require a callback when the scope is cancelled, implement Clearable and declare them with bind Clearable::class. Example:
Declare a Koin scope for nested graph
Instead of scope you can use navGraphScope<AddCitySubgraph>, which handles the lifecycle automatically. Then you can declared your scoped objects inside, as in the previous section.