WezaCare Android Developer Test
User Stories
Build an app using kotlin/Java on android using harry potter data from the Harry Potter public API Requirements:
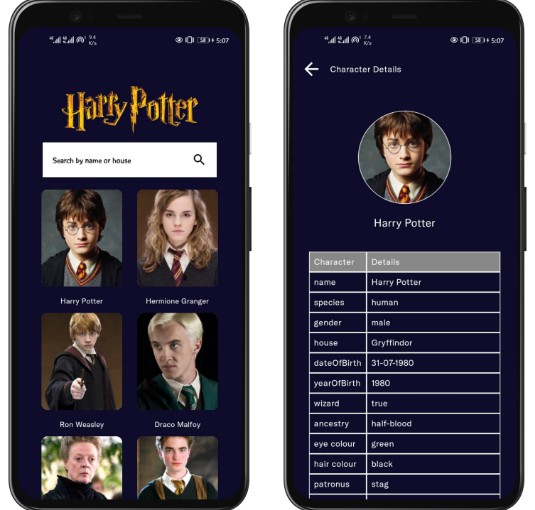
- The app should have a home screen that displays a list of Harry Potter characters retrieved from the API.
- When the user clicks on a character, they should be taken to a detail screen that displays more information about that character, such as their name, role, house, wand, etc.
- The app should have a search functionality that allows the user to search for a specific character by name or house. The search results should be displayed in a list view.
- The app should have a unit test that checks if the API integration is working properly.
Screenshots
I added some screenshots in the screenshots folder, in the root directory of the project to show end to end test on the app.
App architecture
The Android application gathers the layers into three packages:
UI (Presentation) layer
The role of the UI layer (or presentation layer) is to display the application data on the screen. Whenever the data changes, either due to user interaction (such as pressing a button) or external input (such as a network response), the UI should update to reflect the changes.
Domain layer
The domain layer is an optional layer that sits between the UI and data layers. The domain layer is responsible for encapsulating complex business logic, or simple business logic that is reused by multiple ViewModels. This layer is optional because not all apps will have these requirements.
Data layer
The data layer of an app contains the business logic. The business logic is what gives value to your app—it’s made of rules that determine how your app creates, stores, and changes data. The data layer is made of repositories that each can contain zero to many data sources.
Tech Stack.
-
Kotlin – Kotlin is a programming language that can run on JVM. Google has announced Kotlin as one of its officially supported programming languages in Android Studio; and the Android community is migrating at a pace from Java to Kotlin.
-
Jetpack components:
- Jetpack Compose – Jetpack Compose is Android’s modern toolkit for building native UI. It simplifies and accelerates UI development on Android. Quickly bring your app to life with less code, powerful tools, and intuitive Kotlin APIs.
- Android KTX – Android KTX is a set of Kotlin extensions that are included with Android Jetpack and other Android libraries. KTX extensions provide concise, idiomatic Kotlin to Jetpack, Android platform, and other APIs.
- AndroidX – Major improvement to the original Android Support Library, which is no longer maintained.
- Lifecycle – Lifecycle-aware components perform actions in response to a change in the lifecycle status of another component, such as activities and fragments. These components help you produce better-organized, and often lighter-weight code, that is easier to maintain.
- ViewModel -The ViewModel class is designed to store and manage UI-related data in a lifecycle conscious way.
- LiveData – LiveData is an observable data holder class. Unlike a regular observable, LiveData is lifecycle-aware, meaning it respects the lifecycle of other app components, such as activities, fragments, or services. This awareness ensures LiveData only updates app component observers that are in an active lifecycle state.
- Room database – The Room persistence library provides an abstraction layer over SQLite to allow fluent database access while harnessing the full power of SQLite.
- Preferences DataStore – Jetpack DataStore is a data storage solution that allows you to store key-value pairs or typed objects with protocol buffers. DataStore uses Kotlin coroutines and Flow to store data asynchronously, consistently, and transactionally.
-
Kotlin Coroutines – A concurrency design pattern that you can use on Android to simplify code that executes asynchronously.
-
Retrofit – Retrofit is a REST client for Java/ Kotlin and Android by Square inc under Apache 2.0 license. Its a simple network library that is used for network transactions. By using this library we can seamlessly capture JSON response from web service/web API.
-
GSON – JSON Parser,used to parse requests on the data layer for Entities and understands Kotlin non-nullable and default parameters.
-
Kotlin Flow – In coroutines, a flow is a type that can emit multiple values sequentially, as opposed to suspend functions that return only a single value.
-
Dagger Hilt – A dependency injection library for Android that reduces the boilerplate of doing manual dependency injection in your project.
-
Ramcosta Navigation Library – A KSP library that processes annotations and generates code that uses Official Jetpack Compose Navigation under the hood. It hides the complex, non-type-safe and boilerplate code you would have to write otherwise.
-
Logging Interceptor – logs HTTP request and response data.
-
Coil– An image loading library for Android backed by Kotlin Coroutines.
-
Timber– A logger with a small, extensible API which provides utility on top of Android’s normal Log class.
UI and Unit Tests
The screenshot below shows the tests that are done on the repo:
Unit Tests on Network Module
The Unit Tests here test the call to the Harry Potter API