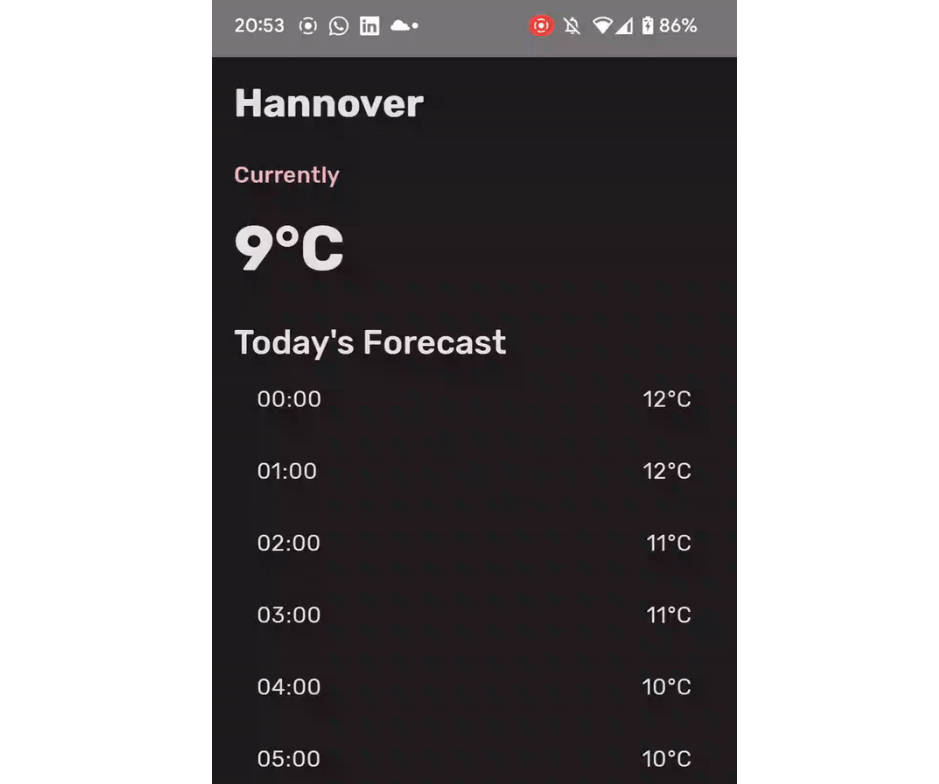
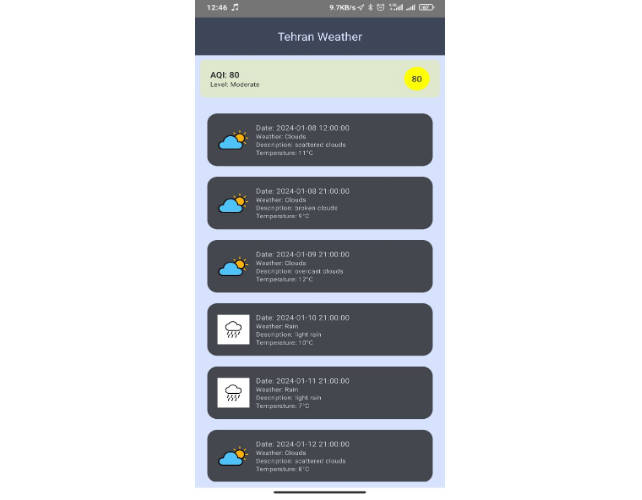
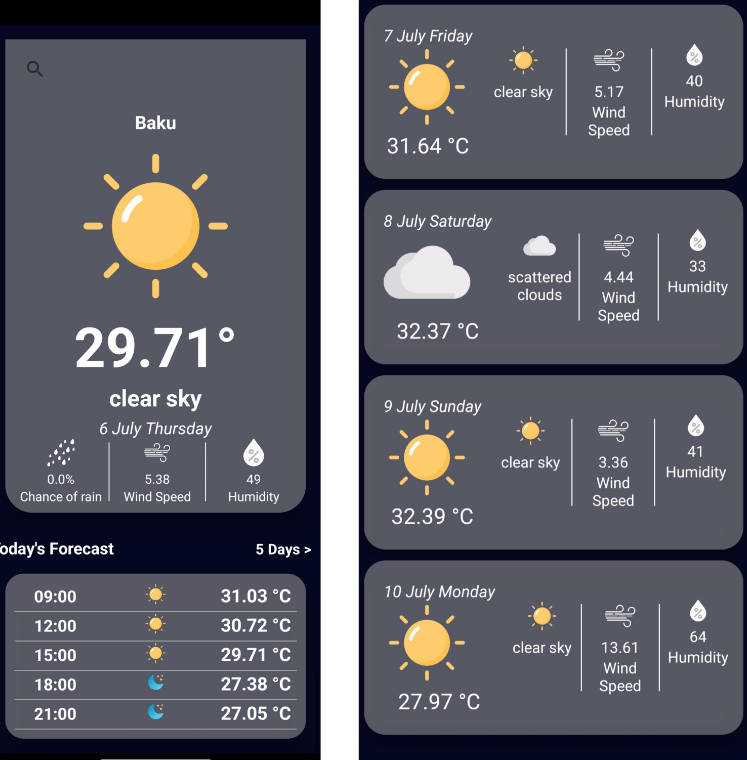
Weather App
Summary
A weather app that displays the forecast for the current day and loads new weather data for different coordinates every 10 seconds.
API : OpenMeteo
Pre-requisite ?
// Built from A.S Giraffe
Design/Architectural decisions ?
The project makes use of common android patterns in modern android codebases.
Project Structure
The folders are split into 4 boundaries:
-
Core:
Contains the models/data classes that are independent of any framework specific dependencies and represent the business logic. In a Clean Arch world you can consider these as your domain classes and interfaces.
-
Data:
Contains data sources , local or remote, this is where the implementation for such is kept. All data related actions and formatting happens in this layer as well. It may contain framework related dependencies to orchestrate and create instances of data stores like a database or shared preference etc. One common pattern used in this area is the repository pattern, which mediates data sources and acts as a source of truth to the consumer.
-
DI:
This acts as the glue between the core ,data and UI.The UI relies on the core models and interfaces which are implemented in data.
-
UI:
Contains the presentation layer of the app, the screen components and viewmodels. Framework specific dependencies are best suited for this layer. In this layer MVI is also used, it looks similar to MVVM but the difference is the actions from a screen a.k.a intents e.g
HomeScreenIntentare predefined and are finite,making the the screen state a bit more predictable and it’s easier to scan through what actions are possible from a given screen.The screen state e.g
HomeScreenViewStateis also modelled as a class with immutable properties and makes state management way easier by reducing the state whenever their is a new update received. Some design patterns that can be seen here are the Observer pattern when consuming the flow -> state flows in the composables and provides a reactive app.
Testing
The data layer is unit tested by mocking out external dependencies i.e The Api Service Interface The ui layer on the viewmodels, has a mix of unit and integration test with the repository being the real one but with swapped dependencies. There are no instrumented or connected tests for now but would be nice for an end to end testing approach.
Technologies ?
Language : Kotlin
Libraries :
UI
-
Data
-
Testing
-
Tooling/Project setup
More to do on this codebase
- Integrate CI Pipeline with lint checks,code formatting and code signing
- Split debug and release build i.e Better app icon for debug and release and other environment settings.
- Time formatting i.e current time, 12hr / 24hr system.
- Look into cache and eviction strategies once it has more data i.e make the app offline first.
- Better issue observability i.e logging errors in Repository on a dashboard somewhere i.e Crashlytics
- Setup for performance monitoring i.e Baseline Profiles, Memory Check i.e leak canary etc & Look into how network and battery consumption is affected by polling.
- Notification for weather alerts and current day forecast.
- Support for a weather widget
- Map and Consume more API data once current feature set is polished i.e Weekly weather information,humidity,wind speed etc.
- Process improvements i.e PR templates/Setup Linting with detekt/ktlint
- Translations for currently supported languages ,i.e strings in res.
- Convert Longitude/Latitude to location name
- Convert hard coded values in the service interface to user preference such as metric vs imperial units.
- Improve UI , have Icons and stuff.
- Use real locations & ability to select multiple locations + setup permissions flow.