PPrint for Kotlin
This is a port of Li Haoyi’s excellent Scala pretty-printing library into Kotlin print. (As well as Li Haoyi’s excellent Ansi-Formatting library Fansi!)
Usage
Add the following to your build.gradle.kts:
implementation("io.exoquery:pprint-kotlin:1.0.0")
Then use the library like this:
import io.exoquery.pprint
data class Name(val first: String, val last: String)
data class Person(val name: Name, val age: Int)
val p = Person(Name("Joe", "Bloggs"), 42)
println(pprint(p))
It will print the following beautiful output:
PPrint-Kotlin supports most of the same features and options as the Scala version. I will document them here over time however for now please refer to the Scala documentation
- For PPrint here – https://github.com/com-lihaoyi/PPrint
- For Fansi here – https://github.com/com-lihaoyi/fansi
Nested Data and Complex Collections
PPrint excels at printing nested data structures and complex collections. For example:
Lists embedded in objects:
data class Address(val street: String, val zip: Int)
data class Customer(val name: Name, val addresses: List<Address>)
val p = Customer(Name("Joe", "Bloggs"), listOf(Address("foo", 123), Address("bar", 456), Address("baz", 789)))
println(pprint(p))
Maps embedded in objects:
data class Alias(val value: String)
data class ComplexCustomer(val name: Name, val addressAliases: Map<Alias, Address>)
val p =
ComplexCustomer(
Name("Joe", "Bloggs"),
mapOf(Alias("Primary") to Address("foo", 123), Alias("Secondary") to Address("bar", 456), Alias("Tertiary") to Address("baz", 789))
)
println(pprint(p))
Lists embedded in maps embedded in objects:
val p =
VeryComplexCustomer(
Name("Joe", "Bloggs"),
mapOf(
Alias("Primary") to
listOf(Address("foo", 123), Address("foo1", 123), Address("foo2", 123)),
Alias("Secondary") to
listOf(Address("bar", 456), Address("bar1", 456), Address("bar2", 456)),
Alias("Tertiary") to
listOf(Address("baz", 789), Address("baz1", 789), Address("baz2", 789))
)
)
println(pprint(p))
Infinite Sequences
Another very impressive ability of PPrint is that it can print infinite sequences, even if they are embedded other objects for example:
data class SequenceHolder(val seq: Sequence<String>)
var i = 0
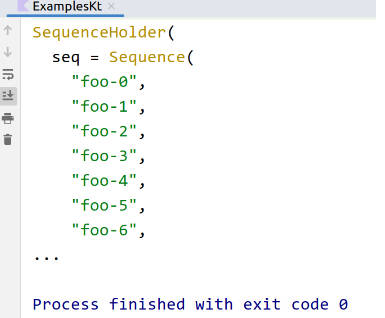
val p = SequenceHolder(generateSequence { "foo-${i++}" })
println(pprint(p, defaultHeight = 10))
PPrint is able to print this infinite sequence without stack-overflowing or running out of memory
because it is highly lazy. It only evaluates the sequence as it is printing it,
and the printing is always constrained by the height and width of the output. You can
control these with the defaultHeight and defaultWidth parameters to the pprint function.
Black & White Printing
The output of the pprint function is not actually a java.lang.String, but a fansi.Str. This means you can control how it is printed. For example, to print it in black and white simple do:
import io.exoquery.pprint.PPrinter
val p = Person(Name("Joe", "Bloggs"), 42)
// Use Black & White Printing
println(pprint(p).plainText)
Removing Field Names
By default pprint will print the field names of data classes. You can remove these by using showFieldNames = false:
val p = Person(Name("Joe", "Bloggs"), 42)
println(pprint(p, showFieldNames = false))
For larger ADTs this dramatically reduces the amount of output and often improves the readability.
Extending PPrint
TODO
Fansi
TODO