Linear Time Picker Library
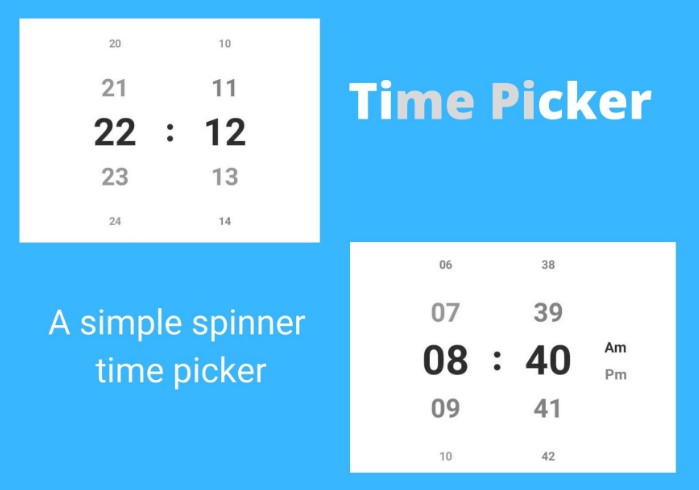
Gorgeous Time and Date picker library inspired by the Timely app.
Stats
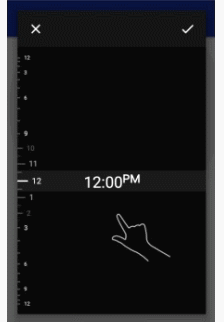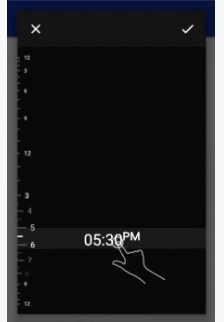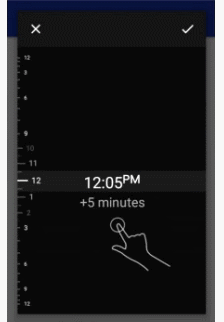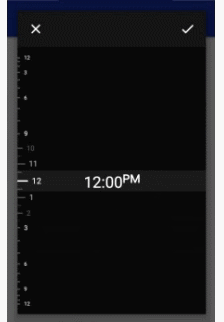
- MinSdk 11
- Unique and intuitive Time and Date pickers
- Gorgeous "grow" effect on the linear dial
- Automated short 10 second tutorial to onboard users
- Customizable to fit your application design
- Occlusion detection
- 24 hour and AM/PM modes based on the device's time settings
- Public API you can use to create your own Linear Picker View
Usage
Step 1
Gradle
Step 2
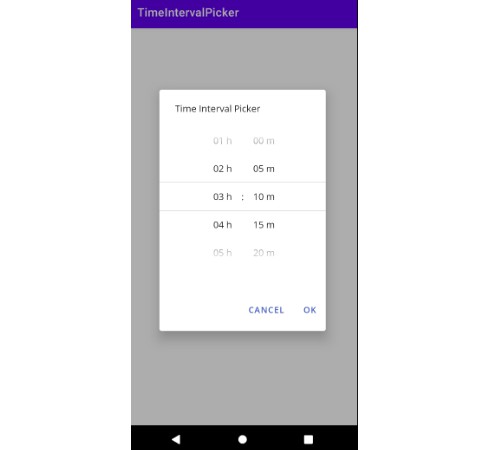
LinearTimePickerDialog
To construct a dialog, the builder pattern is used. The following scaffold contains the minimum code required to construct a dialog.
Showing the dialog is identical to any other Android AlertDialog:
To further customize the LinearTimePickerDialog, the following builder methods are available:

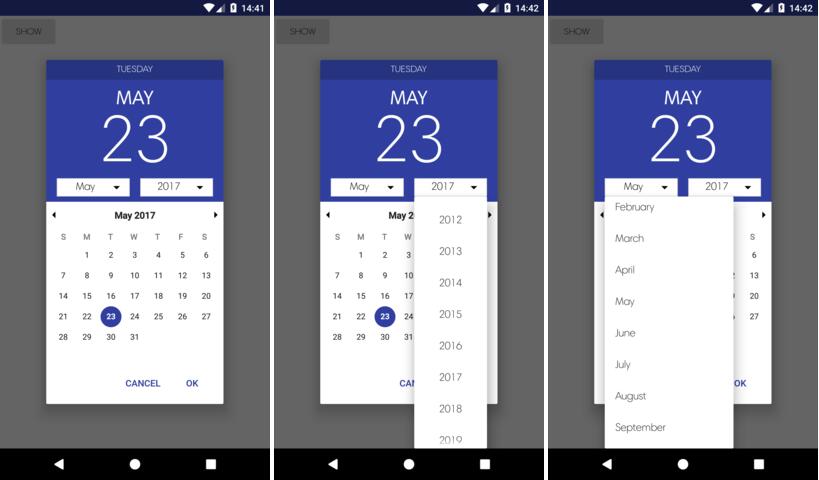
LinearDatePickerDialog
To construct a dialog, the builder pattern is used. The following scaffold contains the minimum code required to construct a dialog.
Showing the dialog is identical to any other Android AlertDialog:
To further customize the LinearDatePickerDialog, the following builder methods are available:

Advanced Usage
For those who want to code their own "Linear Picker View" there is a public API available to build upon:
LinearPickerView
This view can be inflated and appended to a layout. To control what the view draws to the screen a LinearPickerAdapter
should be provided. There are currently 2 ways to create your own adapter.
LinearPickerAdapter interface
This is the most barebones and also most complex way of the two methods. But it allows for the highest level of
customization and can provide stunning results. Following methods have to be implemented:
BaseTextAdapter abstract class
This abstract class implements the required LinearPickerAdapter and provides a complete solution for getting
similar results as the two provided pickers. In case you just want to display a handle with text that scrolls
through a linear dial in which the pips also contain just text, this is an optimal solution.
There's only 5 methods that need to be implemented:
pip
To make use of the adapter in this library it is important you have a good understanding of what the different pip types
are and how each type is addressed.
There are in total 3 pip types:
- Large pip: This is the largest visible pip that signifies a top level entry (e.g. a full hour in the time picker)
- Small pip: This is the smaller visible pip kind that signifies a sub entry (e.g. 30 minute increments in the time picker)
- Invisible pip: These are further sub entries between the different visible pips (e.g. 5 minute increments in the time picker)
Let's assume the following example:
Visible pips are always addressed by using an index relative to the total visible pip count. Above example illustrates how
one would derive the relevant pip from this index.
When an invisible pip is addressed it is always by both the visible pip index described above, and a second step index that
indicates the index of the invisible pip (or step) relative to the visible pip index. It is important to note that
invisible pips do not use an index that is relative to the total amount of pips, as that would be extremely complex to derive
a position from.