CATastrophic
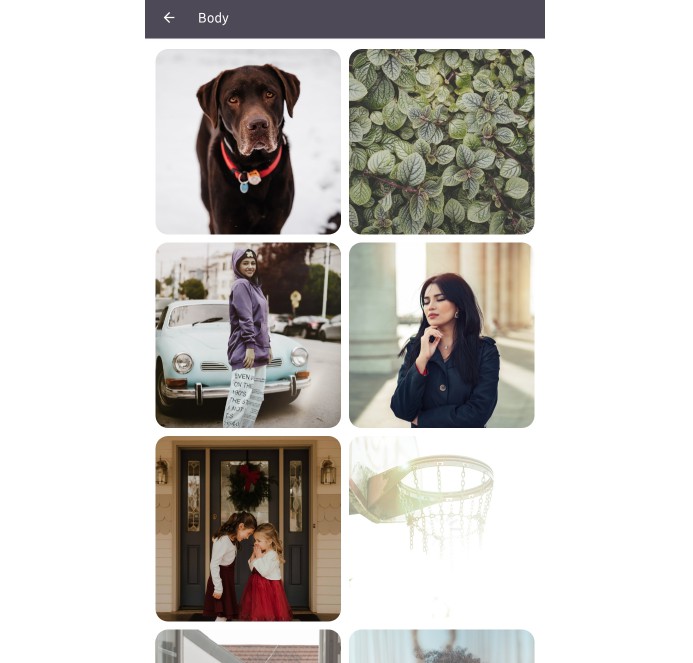
The CATastrophic App is a simple app that shows cat images in a gallery mode. The landing page loads an endless cat images from the cat API in a square-3 column layout.
About the app
It loads the cat images from the remote API, limit each page to 20 images
- Displays the cat images in a square-3 column layout while maintaining the aspect ratio of the image
- Allow the user to browse and scroll through the endless cat images
- Support offline-first architecture for low-speed connections optimization and offline capabilities by storing data in local database
- The app is completely written in Kotlin
- Good test coverage.
App Architecture:
Clean architecture promotes separation of concerns, making the code loosely coupled. This results in a more testable and flexible code. This approach divides the project in 3 modules: presentation, data and domain.
- Presentation: Layer with the Android Framework, the MVVM pattern and the DI module. Depends on domain to access the use cases and on di, to inject dependencies.
- Domain: Layer with the business logic. Contains the use cases, in charge of calling the correct repository or data member.
- Data: Layer with the responsibility of selecting the proper data source for the domain layer. It contains the implementations of the repositories declared in the domain layer. It may, for example, check if the data in a database is up to date, and retrieve it from a service if it’s not. As there isn’t a single way to implement Clean Architecture, this could affront changes in the future.
Tech-stack:
- Written in Kotlin language
- Glide – image loading library for Android.
- Gson – makes it easy to parse JSON into Kotlin objects.
- Hilt- Dependency injector
- Retrofit2- type-safe HTTP client.
- Okhttp3 – an efficient HTTP client for Android and Java applications.
- Coroutines – managing background threads with simplified code and reducing needs for callbacks.
- Coroutines-Flow – suspending functions asynchronously returns a single value, but how can we return multiple asynchronously computed values? This is where Kotlin Flows come in.
- Jetpack:
- AndroidX – major improvement to the original Android Support Library, which is no longer maintained.
- Android Ktx – provide concise, idiomatic Kotlin to Jetpack and Android platform APIs.
- ViewBinding- allows you to bind UI components in your layouts to data sources in your app using a declarative format rather than programmatically.
- Lifecycle
- LiveData
- ViewModel
Testing Frameworks:
- Espresso – to write concise, beautiful, and reliable Android UI tests
- Mockk – provides DSL to mock behavior. Built from zero to fit Kotlin language.
- JUnit – a simple framework to write repeatable tests.
- AndroidX – the androidx test library provides an extensive framework for testing Android apps.