Snitcher captures global crashes, enabling easy redirection to the exception tracing screen for swift recovery
Snitcher
? Snitcher captures global crashes, enabling easy redirection to the exception tracing screen for swift recovery.


What is Snitcher?
Snitcher offers versatile advantages such as aiding in debugging crashes during development, facilitating easy sharing of exceptions by your QA team, enhancing user experiences with recovery screens instead of abrupt closures, and enabling global exception tracing and customized launch behaviors tailored to your specific needs. You have the complete freedom to customize the crash tracing screens according to your build types and preferences, reporting to the Firebase’s Crashlytics with displaying the exception screen, including options like launching a designated Activity, sending messages to your BroadcastReceiver, or any other desired actions.
Documentation
For comprehensive details about Snitcher, please refer to the complete documentation available here.
Download
Gradle
Add the dependency below to your module‘s build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation "com.github.skydoves:snitcher:1.0.0"
}
Usage
Installing Snitcher is a breeze; it hooks into global exceptions, replacing application closure with informative exception tracing screens. You can seamlessly install Snitcher using the following example:
class App : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
Snitcher.install(application = this)
}
}
It’s recommended to install Snitcher on your Application class or your on initialization solution, such as App Startup.
Tracing Global Exceptions
You can trace the global exceptions by providing exceptionHandler lambd parameter. This can be highly beneficial if you intend to gather and report exceptions to other platforms, such as Firebase Crashlyrics.
Snitcher.install(
application = this,
exceptionHandler = { exception: SnitcherException ->
Firebase.crashlytics.log(exception.stackTrace) // or exception.message,
}
)
The exceptionHandler gives you SnitcherException, encompassing the exception message, stack traces, package name, and thread information. Additionally, it enables you to recover the original Throwable instance with the SnitcherException.throwable extension.
Snitcher.install(
application = this,
exceptionHandler = { exception: SnitcherException ->
val message: String = exception.message
val stackTrace: String = exception.stackTrace
val throwable: Throwable = exception.throwable
val threadName: String = exception.threadName
// do somethings
}
)
Custom Exception Trace Screen
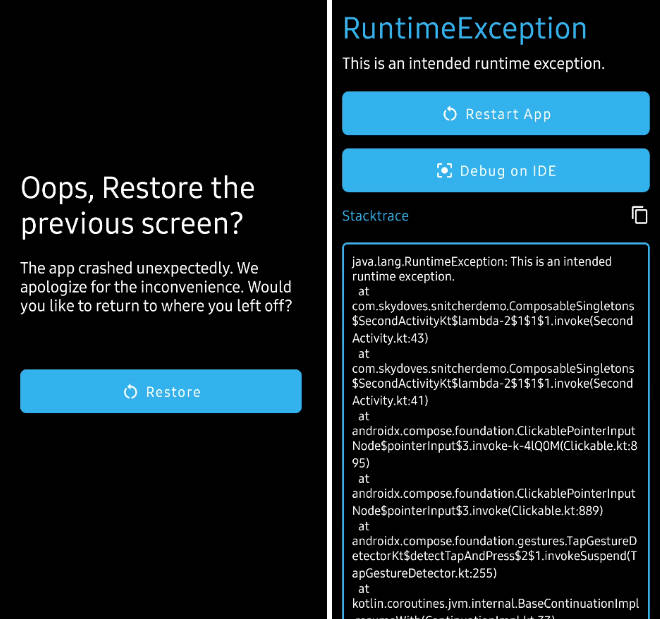
Snitcher provides ready-to-use exception tracing screens (such as ExceptionTraceActivity, built with the ExceptionTraceScreen Composable), giving you the flexibility to extensively tailor these screens according to your preferences, and even design your own distinct tracing interfaces.
Snitcher.install(
application = this,
traceActivity = ExceptionTraceActivity::class
)
If you don’t specify the traceActivity parameter, the default value will be ExceptionTraceActivity. You can tailor the launched activity by modifying the traceActivity parameter to match your preferred choice. The example below demonstrates the construction of a customized trace Activity:
class MyExceptionTraceActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
val exception by Snitcher.exception.collectAsState()
val launcher by Snitcher.launcher.collectAsState()
SnitcherTheme {
if (exception != null) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
// implement your own exception trace screen
ExceptionTraceScreen(
launcher = launcher,
snitcherException = exception!!,
)
} else {
// implement your own app restore screen
AppRestoreScreen(launcher = launcher)
}
}
}
}
}
}
As demonstrated in the example above, Snitcher provides access to the SnitcherException and the package name of the launcher Activity. This information can be utilized to construct highly customized trace screens that align with your specific needs. Snitcher conveniently provides this information through StateFlows, allowing you to observe these values without the need for cumbersome intent handling when initiating the trace Activity.
val exception: SnitcherException? by Snitcher.exception.collectAsState()
val launcher: String by Snitcher.launcher.collectAsState()
Note: Following any app crashes, you can readily observe the exception details across various components at any time and from any location.
Custom Launcher (Restore) Activity
Furthermore, you can customize the launcher (restore activity), specifying which Activity should be executed upon restoration within the trace activity. If you don’t specify a launcher activity, the most recent Activity that encountered a crash will automatically be launched when users press the ‘restore’ button. However, if you wish to launch a particular Activity instead of the most recent one, you can accomplish this by providing the launcher parameter:
Snitcher.install(
application = this,
launcher = MainActivity::class,
)
Custom Snitcher Theme
If you just want to use the pre-builts sreens, but want to customize those components, such as colors and strings, you can easily accomplish it by giving a copy of SnitcherColor to the SnitcherTheme:
SnitcherTheme(
colors = SnitcherTheme.colors.copy(
primary = Color.Blue,
background = Color.White,
textHighEmphasis = Color.Black
)
) {
if (exception != null) {
ExceptionTraceScreen(
launcher = launcher,
snitcherException = exception!!,
)
}
}
If you wish to personalize the text strings within the pre-built UIs, you can override the following string values within your strings.xml file:
<string name="snitcher_release_crash_screen_title">Oops, Restore the previous screen?</string>
<string name="snitcher_release_crash_screen_description">The app crashed unexpectedly. We apologize for the inconvenience. Would you like to return to where you left off?</string>
<string name="snitcher_release_crash_screen_restore">Restore</string>
<string name="snitcher_debug_crash_screen_restore">Restore App</string>
<string name="snitcher_debug_crash_screen_debug_on_ide">Debug on IDE</string>
<string name="snitcher_debug_crash_screen_stacktrace">Stacktrace</string>
Custom Build Types
If you intend to launch distinct trace activities and implement different behaviors or flavors, you can install Snitcher based on specific build types, as shown in the example below:
Snitcher.install(
application = this,
traceActivity = if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
MyExceptionTraceActivity::class
} else {
traceActivity = RestoreActivity::class,
},
exceptionHandler = {
if (!BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Firebase.crashlytics.log(exception.stackTrace)
}
}
)
Alternatively, you can create a single trace Activity and manage the different build types within the activity itself, as demonstrated in the example below:
Snitcher.install(
application = this,
launcher = MyExceptionTraceActivity::class,
)
class MyExceptionTraceActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
val exception by Snitcher.exception.collectAsState()
val launcher by Snitcher.launcher.collectAsState()
SnitcherTheme {
if (exception != null) {
if (Snitcher.isDebuggable) {
ExceptionTraceScreen(
launcher = launcher,
snitcherException = exception!!,
)
} else {
AppRestoreScreen(launcher = launcher)
}
}
}
}
}
}
As demonstrated in the above example, you have the flexibility to create your own trace or restore Activities and install them according to your various build types.
Trace Strategy
You can globally trace exceptions by providing the exceptionHandler lambda parameter during Snitcher installation. However, there might be instances where you don’t wish to launch the trace Activity but rather perform other actions, such as reporting crashes or sending messages to a BroadcastReceiver. In such cases, you can modify the trace strategy as shown in the example below:
Snitcher.install(
application = this,
traceStrategy = TraceStrategy.REPLACE,
exceptionHandler = {
// do something
},
)
In this scenario, only the exceptionHandler lambda function will be executed without triggering the launch of any trace Activity. If the traceStrategy parameter is not specified, the default behavior is set to TraceStrategy.CO_WORK, which involves executing the exceptionHandler lambda and initiating the trace activity when an app crash occurs.
Find this repository useful? ❤️
Support it by joining stargazers for this repository. ⭐ Also, follow me on GitHub for my next creations! ?
License
Designed and developed by 2023 skydoves (Jaewoong Eum)
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.