Material Data Table android library
DataTable
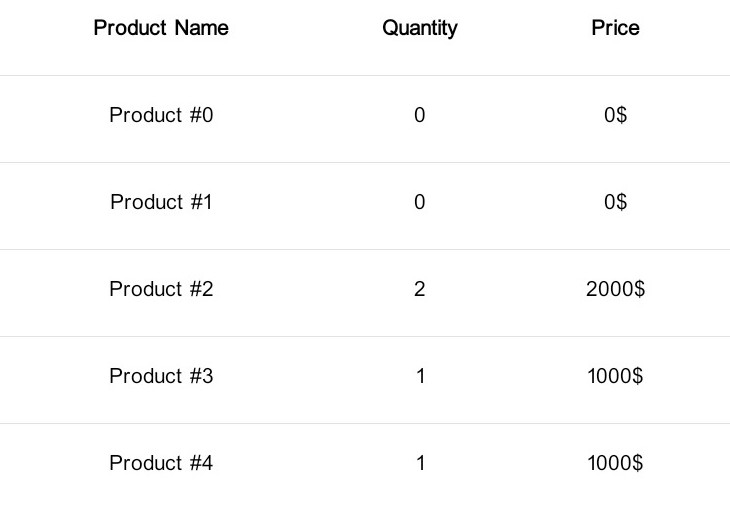
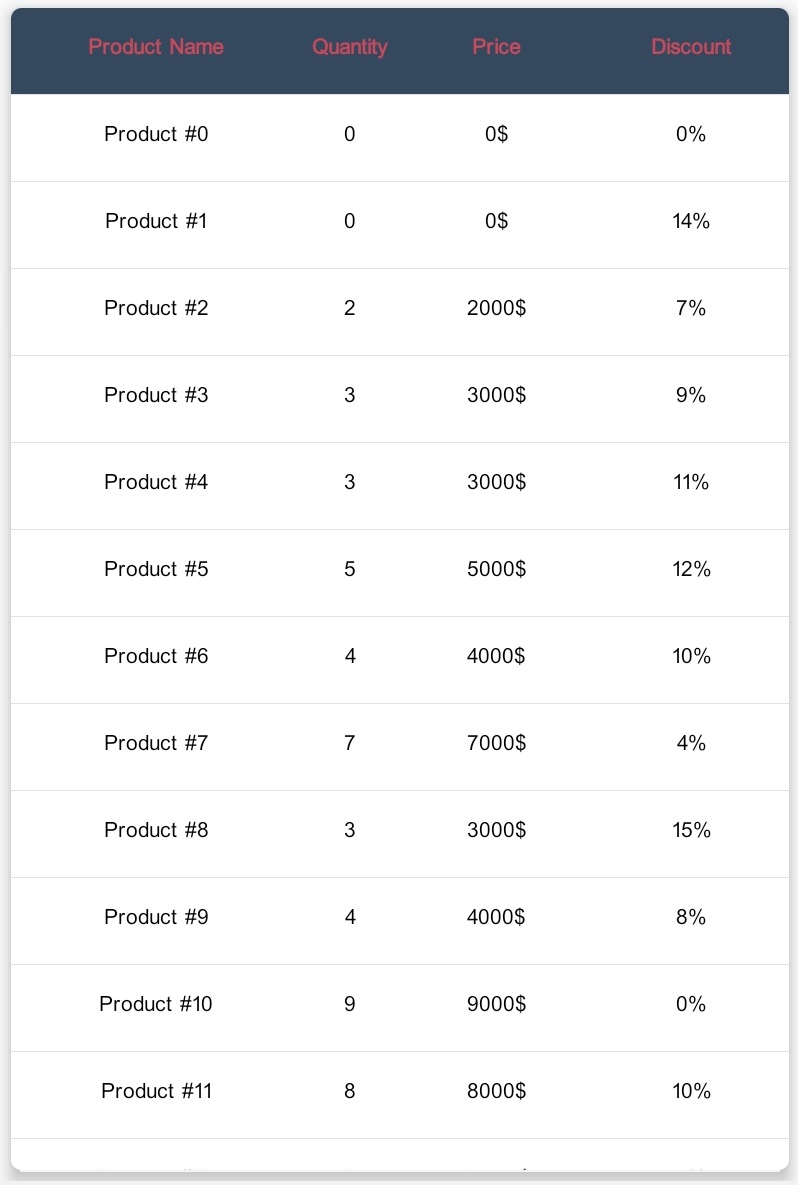
DataTable is a library for create material data table simply. In this version it is only possible to create tables with string values. Soon, image fields, checkbox fields, input fields and etc will be possible.
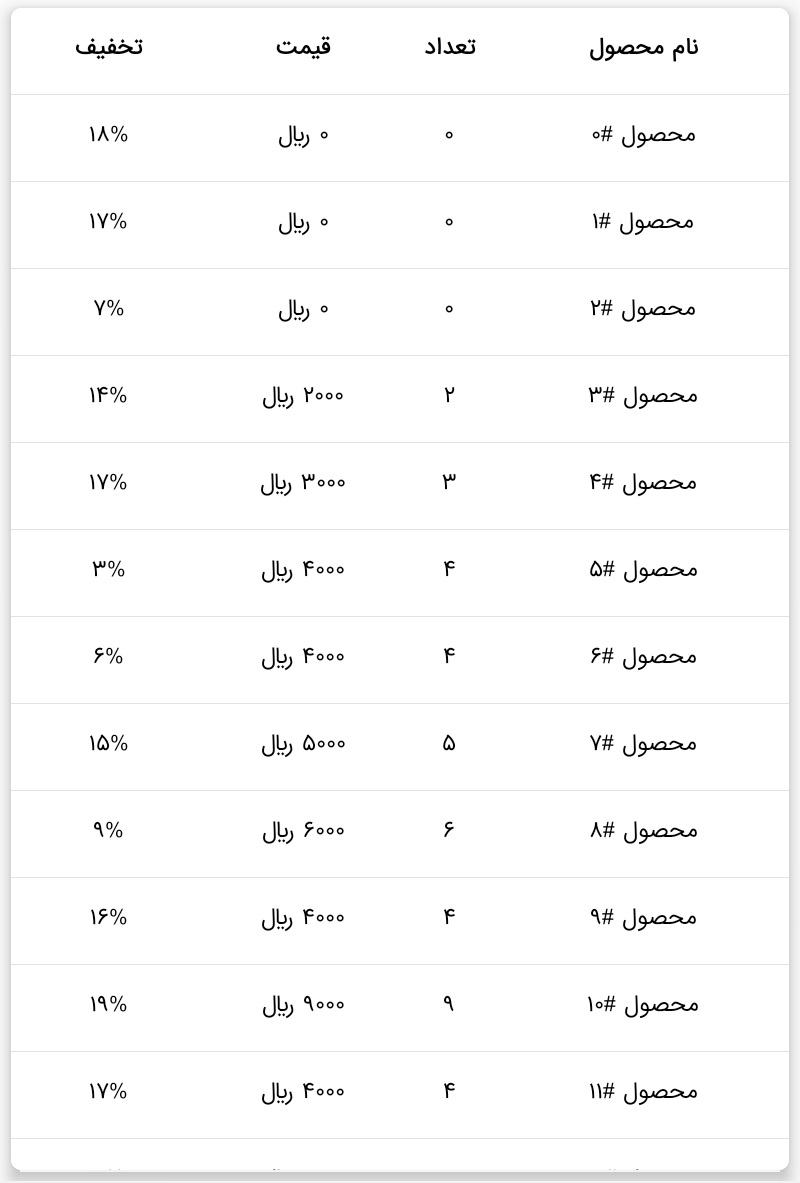
This library is optimized for both ltr and rtl languages
this library is compatible to androidx
Preview
Setup
The simplest way to use this library is to add the library as dependency to your build.
Gradle
Step 1. Add it in your root build.gradle at the end of repositories:
allprojects {
repositories {
...
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}
Step 2. Add the dependency
// builde.gradle(app level)
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.salehyarahmadi:DataTable:v1.0.0'
}
Usage
XML
<ir.androidexception.datatable.DataTable
android:id="@+id/data_table"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
app:header_gravity="center"
app:row_gravity="center"
app:header_vertical_padding="16dp"
app:header_horizontal_padding="0dp"
app:row_vertical_padding="16dp"
app:header_text_size="12sp"
app:row_text_size="12sp"
app:row_text_color="#000"
app:header_text_color="#000"
app:row_background_color="#fff"
app:header_background_color="#fff"
app:persian_number="false"
app:corner_radius="8dp"
app:direction="ltr"
app:shadow="8dp"/>
Java
DataTable dataTable = findViewById(R.id.data_table);
DataTableHeader header = new DataTableHeader.Builder()
.item("field name", field weight)
.item("field name", field weight)
.item("field name", field weight)
.item("field name", field weight)
...
.build();
ArrayList<DataTableRow> rows = new ArrayList<>();
// define 200 fake rows for table
for(int i=0;i<200;i++) {
Random r = new Random();
int random = r.nextInt(i+1);
int randomDiscount = r.nextInt(20);
DataTableRow row = new DataTableRow.Builder()
.value("Product #" + i)
.value(String.valueOf(random))
.value(String.valueOf(random*1000).concat("$"))
.value(String.valueOf(randomDiscount).concat("%"))
...
.build();
rows.add(row);
}
dataTable.setTypeface(typeface);
dataTable.setHeader(header);
dataTable.setRows(rows);
dataTable.inflate(context);
field weight is in integer value for determine field width. This value is relative and field size depends on the weight of the other fields.
For example, if a field weight be 2 and other field weight be 4, This means that the width of the second field is twice that of the width of first field.
Also, you can define unlimited number of fields.
You can set xml attributes programmatically
dataTable.setHeaderTextSize();
dataTable.setRowTextSize();
dataTable.setHeaderTextColor();
dataTable.setRowTextColor();
dataTable.setHeaderBackgroundColor();
dataTable.setRowBackgroundColor();
dataTable.setHeaderVerticalPadding();
dataTable.setHeaderHorizontalPadding();
dataTable.setHeaderVerticalMargin();
dataTable.setHeaderHorizontalMargin();
dataTable.setRowVerticalPadding();
dataTable.setRowHorizontalPadding();
dataTable.setRowVerticalMargin();
dataTable.setRowHorizontalMargin();
dataTable.setHeaderGravity();
dataTable.setRowGravity();
dataTable.setDividerThickness();
dataTable.setDividerColor();
dataTable.setCornerRadius();
dataTable.setShadow();
dataTable.setDirection();
dataTable.setPersianNumber();