Github API consumer to list user repositories using SpringBoot with Spring WebFlux
GitHub Repositories Lister
This project uses SpringBoot and Spring WebFlux to list the repositories of a user which are not forks along with its branches.
Building the application
To build application and package it as an executable jar, simply run
./gradlew clean check bootJar
You can find the generated jar in ./build/libs
with the name github-lister-boot.jar
Running the application
To run the application, first you need to create a github access token. Follow this guide to know more.
After you acquire an access token, you can either:
- Run the application without building by running
./gradlew bootRun \
--args='--github.api.accessToken=<your-access-token>'
- Build the application then run the generated jar file using
./gradlew java -jar \
-D'github.api.accessToken=<your-access-token>' \
./build/libs/github-lister-boot.jar
Packaging a containerized application
To build and publish the application as docker container, a Dockerfile is provided.
You can use the following command to create the container
after replacing the <image-name> and <image-tag> with your values
docker build -t <image-name>:<image-tag> .
The docker file is using 2 stages, one for building and another one for the runnable container. The order of the steps is important to minimize the number of layers that needs to be re-created.
The first stage is using a base JDK container structured to :
- Copies the required files for a gradle build
- Download gradle and the dependencies using
./gradlew dependencies - Copy the application source code
- Build the application using
./gradlew bootJar
The second stage is using a smaller base container with only the JRE structured to:
- Copies the built jar from the previous stage
- Creates the entry point of the container
- Exposes the
8080port which is the server port
Deploying to AWS
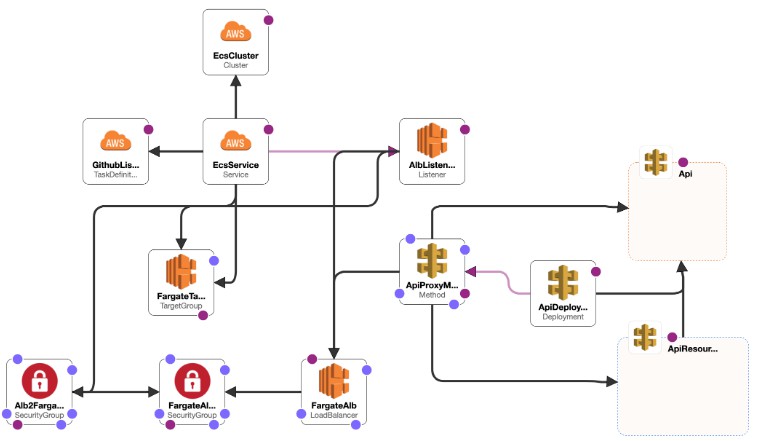
To deploy the application to AWS, a cloud formation template cf-stack.yaml is created.
The template creates the resources shown in the diagram
To deploy the template, you can use
aws cloudformation --region <aws-region> deploy --template-file cf-stack.yaml --stack-name <stack-name>
The template does not create a VPC or subnets. It already uses the default VPC and subnets in the region. You will need to provide the following parameters to be able to run the template
- ExecutionRole: This is used to give ECS service the permission to create tasks. See here on how to create ECS task execution role
- ContainerImage: The full name of the application docker image.
- GithubAccessToken: The token that the application use to access GitHub APIs
- AwsLogsGroup: Logs group name that the app will create to retain the logs of the application
- VpcId: The id of the VPC in the region in which you are deploying the stack
- SubnetOne: The id of one of the subnets in the same VPC added before
- SubnetTwo: The id of another subnet in the same VPC added before