Dynamic control over vector drawables
VectorMaster
This library introduces dynamic control over vector drawables. Each and every aspect of a vector drawable can be controlled dynamically (via Java instances), using this library.
Features :
- Control : Control every attribute related to
path,group,vectorandclip-pathlike color, alpha, strokeWdith, translation, scale, rotation etc. - Clip Paths : The library supports clip paths.
- Trimming : The library allows trimming of path by using
trimEnd,trimStartandtrimOffsetparameters.
Usage
Just add the following dependency in your app's build.gradle
dependencies {
compile 'com.sdsmdg.harjot:vectormaster:1.1.3'
}
Background and Working
VectorDrawables are really helpful for removing scaling problem but they lack control. Most of the changes to vector drawables are only possible by creating an AnimatedVectorDrawable and also defining animations. All of this is good but lacks control that may be required during runtime.
For example, if we need to change vector's properties (Say, color) based on a user action (Say, if user is choosing the theme of app). We can achieve this using AnimatedVectorDrawable but only to an extent, this approach can't be used if user action leads to an infinite number of cases (Say, if user picks up a random color for theme) and we need to change property of the vector for each case. Thus we need a mechanism that can be used to change a vector's properties at runtime using basic methods like setColor, setScale, setTranslation etc. This is where this library comes in.
The library works as follows :
- First the
vector.xml(theVectorDrawablethat we wish to control), is parsed usingXmlPullParserand the attributes are stored in Models corresponding to the tag. vectorattributes are stored inVectorModel,groupattributes inGroupModel,pathatrributes inPathModelandclip-pathattributes inClipPathModel. The hierarchy is as follows :
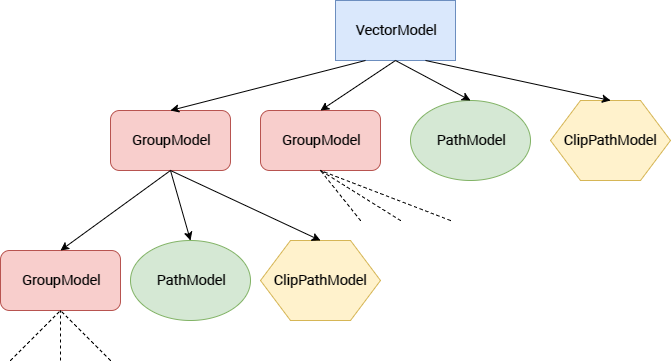
- The
pathDatainPathModelis then parsed usingPathParser.java; It parses the string data and converts it into aPathobject. - All the transformations, scaling etc are done using Matrices after the
Pathobject is built. All this is done prior to the first draw on canvas. - At first draw we have the same output as we should have got if we used inbuilt methods to draw the
vector.xmlusingsrcCompat. - Now, all Models are accessible via
getModelByName(...)public methods that can be directly called via the instance ofVectorMasterViewthat we get usingfindViewById(...). - If we wish to change any value, we just need to call
model.setParamter(...).modelis of typeVectorModel,GroupModel,PathModelorClipPathModel.parametercan be anything like color, scale, rotation etc. depending on the model we are using. - After setting a paramter the necesarry
paintsandpathsare rebuilt, scaled, transformed etc. - A call to
updatemethod repaints the canvas with the required changes.
Examples
ic_heart.xml (This is the original vector that has been used in all examples)
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="24dp"
android:height="24dp"
android:viewportWidth="24.0"
android:viewportHeight="24.0">
<path
android:name="outline"
android:pathData="M20.84,4.61a5.5,5.5 0,0 0,-7.78 0L12,5.67l-1.06,-1.06a5.5,5.5 0,0 0,-7.78 7.78l1.06,1.06L12,21.23l7.78,-7.78 1.06,-1.06a5.5,5.5 0,0 0,0 -7.78z"
android:strokeLineCap="round"
android:strokeColor="#5D5D5D"
android:fillColor="#00000000"
android:strokeWidth="2"
android:strokeLineJoin="round"/>
</vector>
Example 1 (Simple Color change)
XML
<com.sdsmdg.harjot.vectormaster.VectorMasterView
android:id="@+id/heart_vector"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
app:vector_src="@drawable/ic_heart" />
Java
VectorMasterView heartVector = (VectorMasterView) findViewById(R.id.heart_vector);
// find the correct path using name
PathModel outline = heartVector.getPathModelByName("outline");
// set the stroke color
outline.setStrokeColor(Color.parseColor("#ED4337"));
// set the fill color (if fill color is not set or is TRANSPARENT, then no fill is drawn)
outline.setFillColor(Color.parseColor("#ED4337"));
Result
Example 2 (Trim paths)
XML
<com.sdsmdg.harjot.vectormaster.VectorMasterView
android:id="@+id/heart_vector"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
app:vector_src="@drawable/ic_heart" />
Java
VectorMasterView heartVector = (VectorMasterView) findViewById(R.id.heart_vector);
// find the correct path using name
PathModel outline = heartVector.getPathModelByName("outline");
// set trim path start (values are given in fraction of length)
outline.setTrimPathStart(0.0f);
// set trim path end (values are given in fraction of length)
outline.setTrimPathEnd(0.65f);
Result
Example 3 (Simple color animation using ValueAnimator)
XML
<com.sdsmdg.harjot.vectormaster.VectorMasterView
android:id="@+id/heart_vector"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
app:vector_src="@drawable/ic_heart" />
Java
VectorMasterView heartVector = (VectorMasterView) findViewById(R.id.heart_vector);
// find the correct path using name
PathModel outline = heartVector.getPathModelByName("outline");
outline.setStrokeColor(Color.parseColor("#ED4337"));
heartVector.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// initialize valueAnimator and pass start and end color values
ValueAnimator valueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new ArgbEvaluator(), Color.WHITE, Color.parseColor("#ED4337"));
valueAnimator.setDuration(1000);
valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
// set fill color and update view
outline.setFillColor((Integer) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue());
heartVector.update();
}
});
valueAnimator.start();
}
});
Result
Example 4 (Simple trim animation using ValueAnimator)
XML
<com.sdsmdg.harjot.vectormaster.VectorMasterView
android:id="@+id/heart_vector"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
app:vector_src="@drawable/ic_heart" />
Java
VectorMasterView heartVector = (VectorMasterView) findViewById(R.id.heart_vector);
// find the correct path using name
PathModel outline = heartVector.getPathModelByName("outline");
outline.setStrokeColor(Color.parseColor("#ED4337"));
outline.setTrimPathEnd(0.0f);
heartVector.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// initialise valueAnimator and pass start and end float values
ValueAnimator valueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0.0f, 1.0f);
valueAnimator.setDuration(1000);
valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
// set trim end value and update view
outline.setTrimPathEnd((Float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue());
heartVector.update();
}
});
valueAnimator.start();
}
});
Result
Complex animations
The above examples are just the basic use cases and are meant to serve as a quick start to using the library. For more complex animations and use cases involving clip-paths and groups, head to AnimationExamples
If your animation doesn't involve any clip-path or group, then you may use RichPath library developed by tarek360. This library is really useful, if you don't want to indulge in too much mathematics or logic.
Using as a Custom Drawable
The library also provide custom drawable implementation in form of VectorMasterDrawable. It provides the same control over the vector, but allows the user to use the drawable as per its wish, for e.g. as a Compound Drawable in TextView, or as the source drawable in ImageView; basically any use case that involves a Drawable can be replaced by VectorMasterDrawable.
Example
XML
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Heart"
android:textSize="30sp" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image_view"
android:layout_width="75dp"
android:layout_height="75dp"/>
Java
// Instantiate the custom drawable
VectorMasterDrawable vectorMasterDrawable = new VectorMasterDrawable(this, R.drawable.ic_heart);
// Set top drawable for TextView
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_view);
textView.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(null, vectorMasterDrawable, null, null);
// Set background drawable for ImageView
ImageView imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image_view);
imageView.setImageDrawable(vectorMasterDrawable);
// Set tht stroke color of the drawable
PathModel pathModel = vectorMasterDrawable.getPathModelByName("outline");
pathModel.setStrokeColor(Color.parseColor("#ED4337"));