A sample project that helps to start building a Mobile Kotlin Multiplatform application
Mobile Kotlin multiplatform project template
A sample project that helps to start building a Mobile Kotlin Multiplatform application. It establishes an architecture optimized for building cross-platform mobile applications through separation of concerns between the UI and business logic.
Table of Contents
Features
- Kotlin Multiplatform‘s motto is Don’t Repeat Yourself. Share the business logic code written in Kotlin between Android and iOS apps. 100% native UI and performance (shared code compiles into native libraries);
- Kotlin Gradle DSL – Configure project with flexible Kotlin Gradle DSL;
- Modular-bazed architecture – Implement app features independently of each other. Inject dependencies into features at compile-time through the use of the
Factoryclass; - Parallel build of modules – Feature modules and the
domainmodule don’t depend on each other. This provides caching of build artifacts for each module and results in better compilation time; - Dependencies definition in buildSrc – Simplify dependency management across modules;
- Ready to use – Template project includes all moko libraries and supports most common use cases:
- ViewModels;
- LiveData;
- Resource management;
- Runtime permissions access;
- Media access;
- UI lists management from shared code;
- Network layer generation from OpenAPI.
Modules
Legend
The color describes different modules and the shape – the type of an element (class|interface).
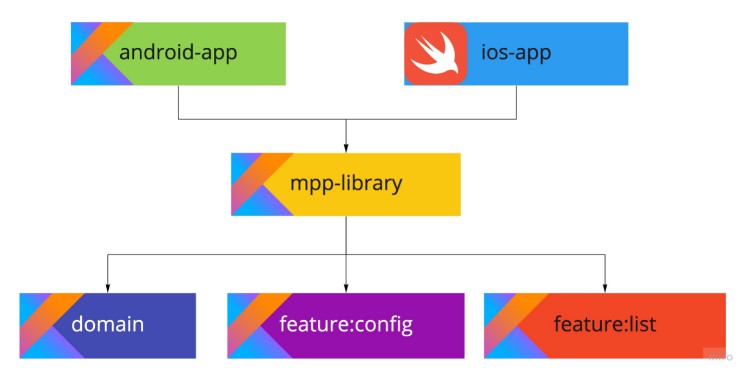
Modules scheme
This scheme shows the structure of the project:
- We have two applications that represent the View application layer:
android-appwritten in Kotlin usesActivityandFragment;ios-appwritten in Swift usesUIViewControllerwith Storyboards.
- Both applications depend on
mpp-library(Kotlin Multiplatform) that provides access toViewModel‘s of each feature throughSharedFactory. The library is responsible for setting up connections between thefeatureanddomainmodules. mpp-libraryconsists of modules:domain(Kotlin Multiplatform) – contains the domain entities, repositories, server API classes, andDomainFactorythat creates instances for all of them;feature(Kotlin Multiplatform). Every feature contains corresponding ViewModel, Factory, models, and interfaces it expects to be injected from the parent module. In this example:configcontains an config feature’s ViewModel, data store interface andConfigFactorythat create instances of ViewModel;listcontains a items list feature’s ViewModel, data source interface, list items factory interface, andListFactorythat create instances of ViewModel.
Config module scheme
The connections between the feature:config classes and the domain classes implemented in the mpp-library module.
List module scheme
The connections between the feature:list classes and the domain classes implemented in the mpp-library module.
SharedFactory.NewsUnitsFactory interface is implemented on both platforms – Android (android-app) and iOS (ios-app).
Screenshots
| Android | iOS |
|---|---|
How to Run
Android – just open repository root directory in Android Studio and press Run.
iOS – run pod install in directory ios-app. Then open ios-app/ios-app.xcworkspace and press Run on simulator/device.
Project setup
Setup your own ApplicationId
Just like in other native apps
In android-app/build.gradle.kts change org.example.app in the following line:
applicationId = "org.example.app"
In Xcode project settings change Bundle Identifier.
Setup your own project name
Just like in other native apps
In android-app/src/main/res/values/strings.xml change value of app_name.
In Xcode project settings change Display name.
Setup your own app icon
Just like in other native apps
Put your android icon to android-app/src/main/res and setup usage in android-app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml.
Put your iOS icon to ios-app/src/Assets.xcassets/AppIcon.appiconset.
Create new feature module
Create a file mpp-library/feature/myfeature/build.gradle.kts with the following content:
plugins {
id("multiplatform-library-convention")
}
Add module to settings.gradle.kts:
include(":mpp-library:feature:myfeature")
Add dependency to module from the mpp-library in mpp-library/build.gradle.kts:
framework {
...
export(projects.mppLibrary.feature.myfeature)
}
Contributing
All development of template is performed in the master branch. Please send PRs with bug fixes to the master branch.
Please refer to the contributing guide for more details.
Thanks
We test Apple Silicon support with MacStadium.
License
Copyright 2019 IceRock MAG Inc
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
